I was hired to streamline usability research on existing Macmillian educational products as well as assist in the creation of Macmillan learnings first onsite Learning Lab that will enable learning researchers and human-centered designers to co-design and iteratively test with students and instructors.
Where: Macmillian Learning In-house
Role: User Experience Research
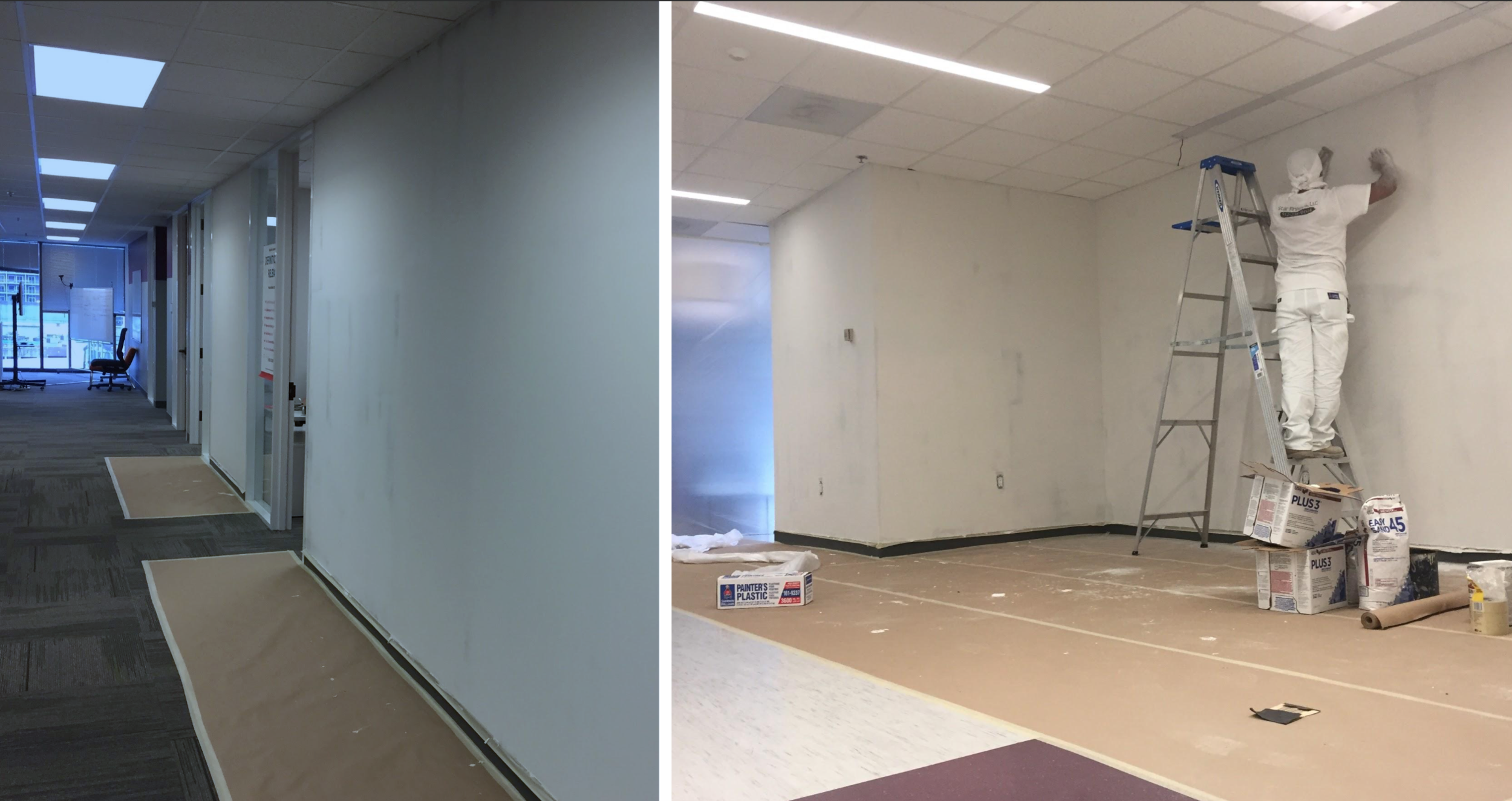
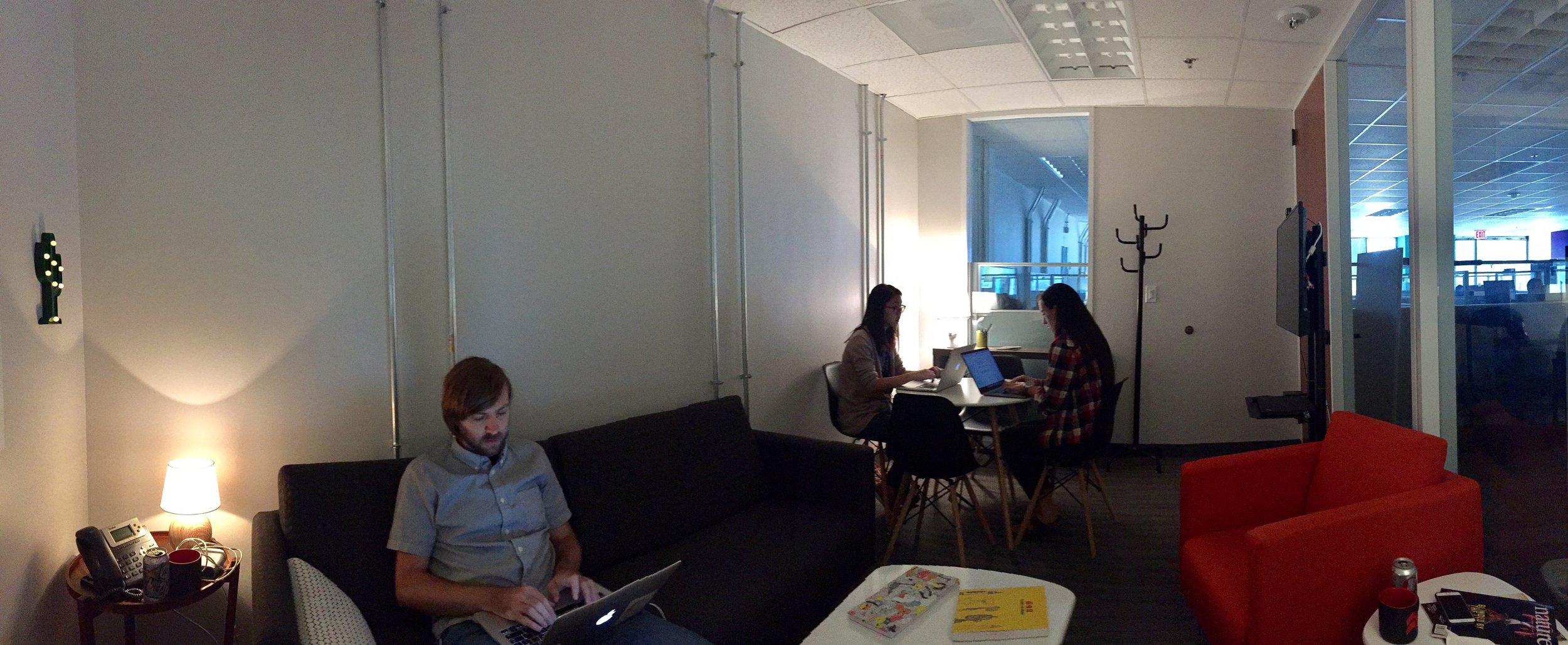
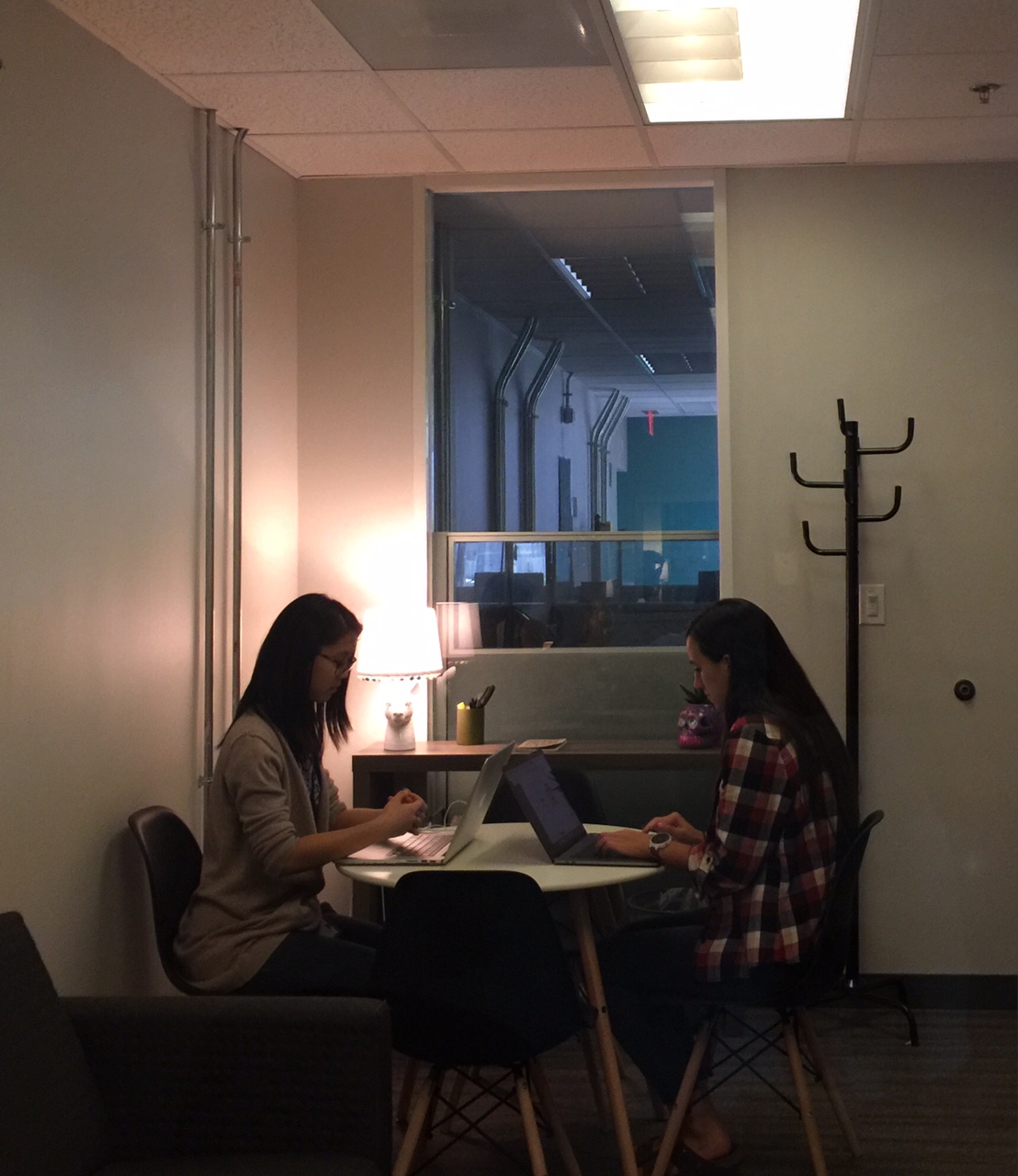
Assisted in the design and execution of Macmillan’s first combined user-centered design and learning science lab. The Lab was designed to enable learning researchers and human-centered designers to co-design and iteratively test with students and instructors to create learning products that are usable and highly impactful. It consists of adjoining observation room, remote broadcast capabilities, and usability software. It was also designed to support neurological and biometrics technology to enable researchers to study affective, cognitive, and physiological responses to product designs.
Wrote the procedural manual for recruitment process & scheduling of participants. Streamlined participant onboarding, compensation and retention. Guided development of participant screeners that are relevant to each research project.
Collaborated with product managers, product designers, UX designers, and other researchers to strategize and design research activities using user-centered design. This included identification of user needs and goals, task and workflow modeling, ethnography and persona development.
Designed and distributed surveys. Conducted moderated and unmoderated usability research (Recruiting, interviewing, note-taking, debriefing, observation, and data collection) both online and in the field.
Project Example
Project: Launch of the Macmillian Learning Lab
Press: Macmillan Launches Austin Learning Lab
Duration: 6 Months
Macmillan Learning improves lives through learning. Their legacy of excellence in education informs their approach to developing world-class content with pioneering, interactive tools. Through deep partnership with the world’s best researchers, educators, administrators, and developers, they facilitate teaching and learning opportunities that spark student engagement and improve outcomes.Macmillan Learning provides educators with tailored solutions designed to inspire curiosity and measure progress.
WHY A LAB?
Research shows that teams make better products when everyone on a project team observes research first hand. Watching people engage in real time with the services we design brings insight and empathy to our work, a quality that cannot be replicated by reports, graphs, or presentations.
By making lab sessions more easily accessible, we’re able to regularly involve team members early on in the research process. This encourages those same team members to be involved in research analysis, and therefore more informed in the design decisions.
UX Research supports Agile Design and Development: Design, prototype, get quick feedback, make decisions and iterate in rapid sprints.
The lab was designed based upon highly successful labs at IBM and the National Cancer Institute, principles of environmental design, and consultation with leading expert Dr. Robert Atkinson, the Director of Arizona State University’s Advancing Next Generation Learning (ANGLE) Lab.
“Labs enable researchers to simulate learning environments, to introduce new features into these environments, and then observe and record how learners’ respond in order to optimize the environments’ ability to support learning. It’s exciting to see Macmillan making strides in this area, and I’m glad to be able to help them design research methods as well as research tools for the Learning Lab.”
Research is a team sport
Research shows that teams make better services when everyone on a project team observes users first hand. Watching people engage in real time with the services we design brings insight and empathy to our work, a quality that cannot be replicated by reports, graphs or presentations. As a result, we tried to make sure that all team members had easy access to the testing either remotely or live, to watch at least 2 hours of research every 6 weeks.
A big part of helping team members gain these 'exposure hours' is to make real-time user research more easily visible and accessible. Having a lab in-house is a vital part of this. Our team members no longer need to be invited to research to know it's happening and they don't need to commute to an external lab. They need only view the lab calendar and click the link the live stream from their office or conference room as a team or they can clear a couple hours from their schedule, and pop down stairs.
Different people remember different details – encouraging everyone who watched a session to join the analysis helps us gather more information and perspectives. Everyone who’s invested in the project participates and understands the outcomes providing easier decisions on what to do next.
“Cancer has a journey and we wanted to create a lab to capture the substance of that journey, understand what is needed and help design technologies to support people affected by cancer.”
By making lab sessions more easily accessible, we’re able to more regularly involve team members early on in the research process. This in turn encourages those same team members to be more involved in research analysis and, therefore, more informed in the making of design decisions. Suddenly, the whole team is responding personally to user needs. Research is no longer a report sitting on a desk or in an email but a living-and-breathing experience: watching people informs the team and we're making it easy.
Take away: Characteristics & Trends
Characteristics
Reliable
Trustworthy
Simple to use
Versatile between Studies
High quality output
Accessible output-Files & viewing
Trends
Benchmarking for comparison
Integrations with analytics to action results Utilize multiple research methods
Remote, viewing and interviewing
Projects that evaluate or validate design patterns
Mobile
In-House Labs
Austin LUX: Lab
The Austin Learning Lab is the first in a series of new labs that will enable learning researchers and human-centered designers to co-design and iteratively test with students and instructors to create learning products that are highly usable and highly impactful. The lab comprises an adjoining observation room, remote broadcast capabilities, and usability software. It is also designed to support neurological and biometrics technology and will expand to enable researchers to study affective, cognitive, and physiological responses to product designs.
The Lab will enable Macmillan to strengthen its leadership in learning research by modeling learning, blending innovative research methods into actionable results, and fostering a culture of research inclusivity and collaboration.
“Our labs reflect our focus on and commitment to the learner. These facilities put learners at the center of our research and design teams and enable us to engage with our users as co-designers on a daily basis.”
Focus and Goals of the lab
Modeling Learning. The lab provides a space in which to model learning with an individual or small group in a controlled setting. Combining tightly controlled lab work with on-campus field research with partner instructors and institutions enables researchers to compare how learning experiences work under ideal and real circumstance, and make refinements accordingly.
Blending Innovative Methods into Actionable Results. In the lab, researchers can bring together methods from different disciplines, including educational research, human-computer interaction, and data science. These “blended” methods enable researchers to draw connections between formerly disparate concepts, such as usability and learning impact. The subsequent pairing of attitudinal and observational research with biometrics and just-in-time analytics will offer a thorough view into student performance that can be immediately applied to product design, iteration, and optimization.
Fostering Research Inclusivity and Collaboration. The lab is also designed to enable more teams from across Macmillan Learning to participate in research, and to fully understand how instructors and learners are engaging with products. This transparency and collaboration will enable teams to learn from results and customer insights much faster
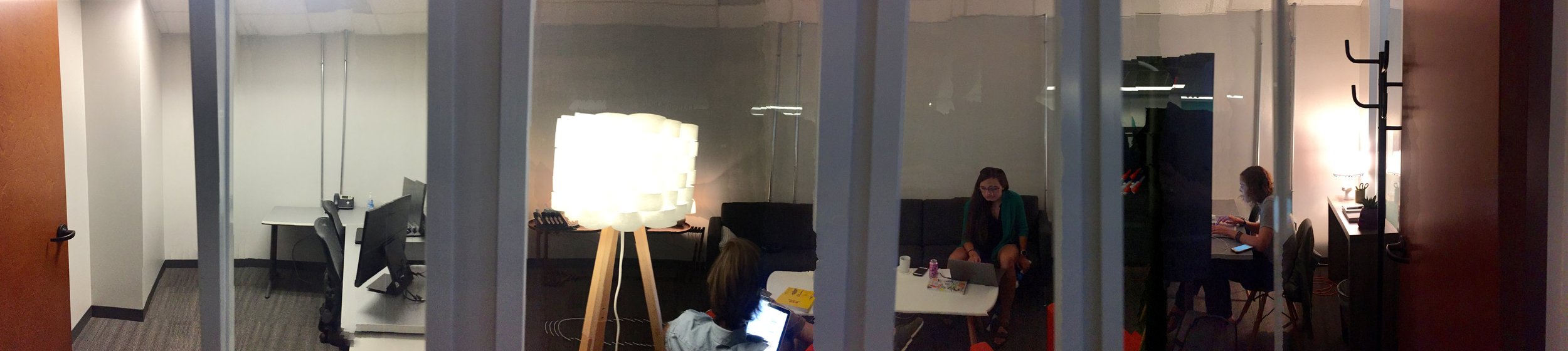
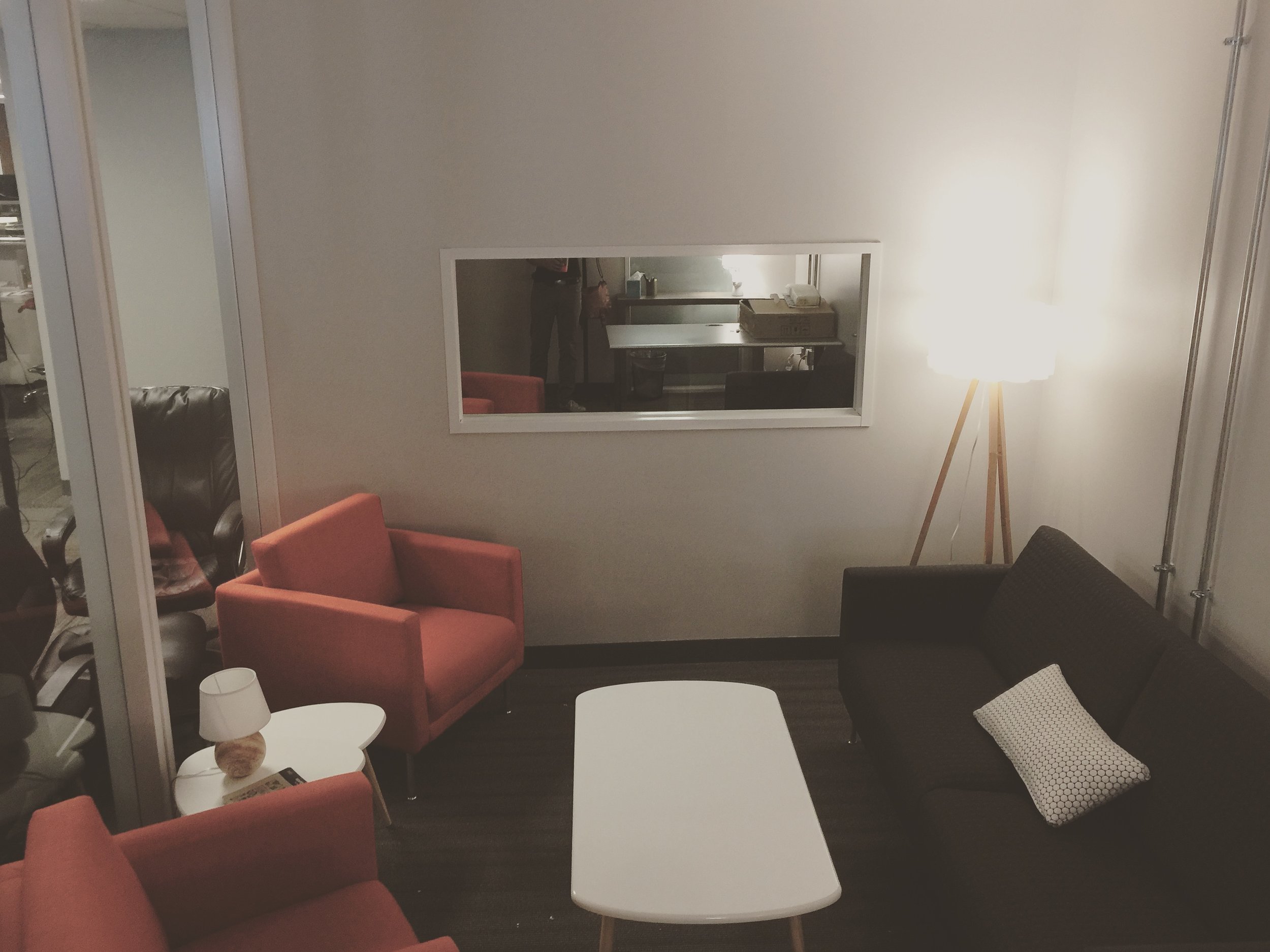
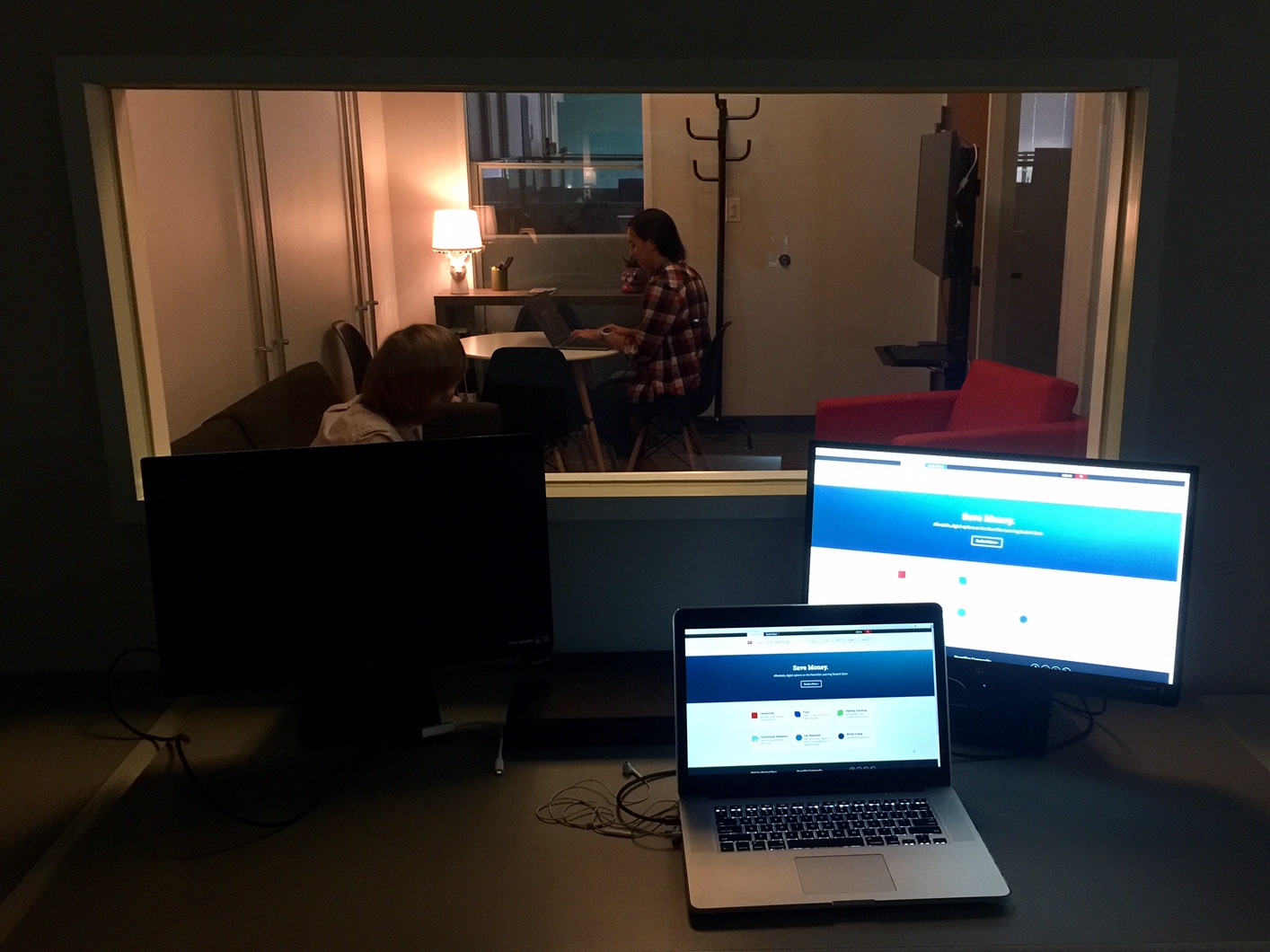
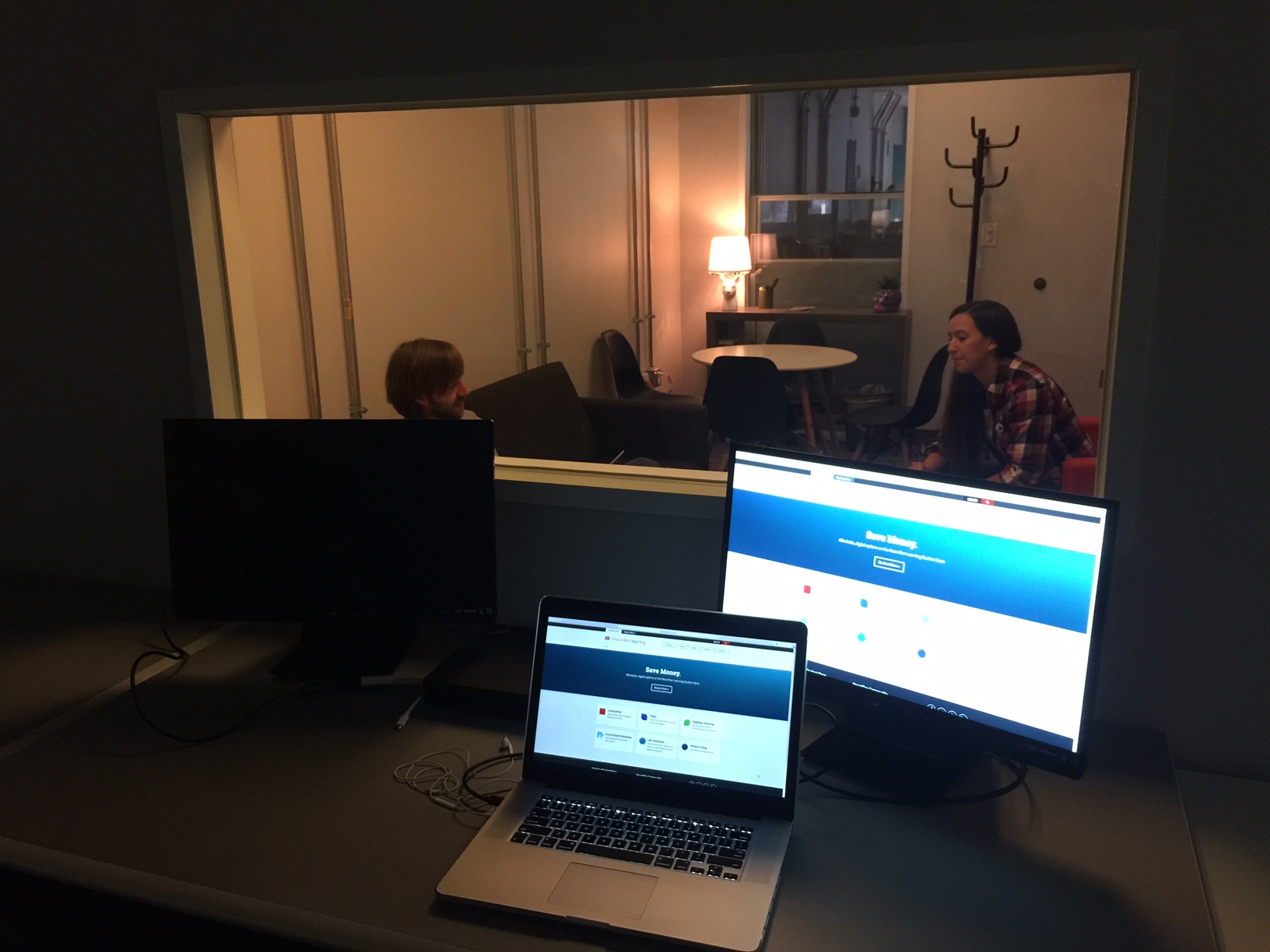
The Elephant in the room... One-way glass
A large one-way mirror between the user and observation rooms allows direct observation of participants, plus a dedicated monitor in the observation room provides a live onscreen view of exactly what the participant sees, along with a picture-in-picture of the participant’s face. This arrangement provides the team a clear view of the participants’ facial expressions and their behavior. The sessions are recorded with state-of-the-art software that combines video, audio and logging notes for analysis and creating video clips.
The main reason for using a research facility with a view-through mirror is being able to invite designers, stakeholders, and engineers to observe how participants react to our products and services.One-way glass is transparent on one side but opaque on the other. It's often used in research labs and allows observers to watch participants without being seen. There’s a lot to think about when deciding on one-way glass. During conversations with existing UX labs I came across several labs who’ve had to rethink and replace their glass until they’ve got it right.There’s also the privilege of keeping it sparkling clean too.
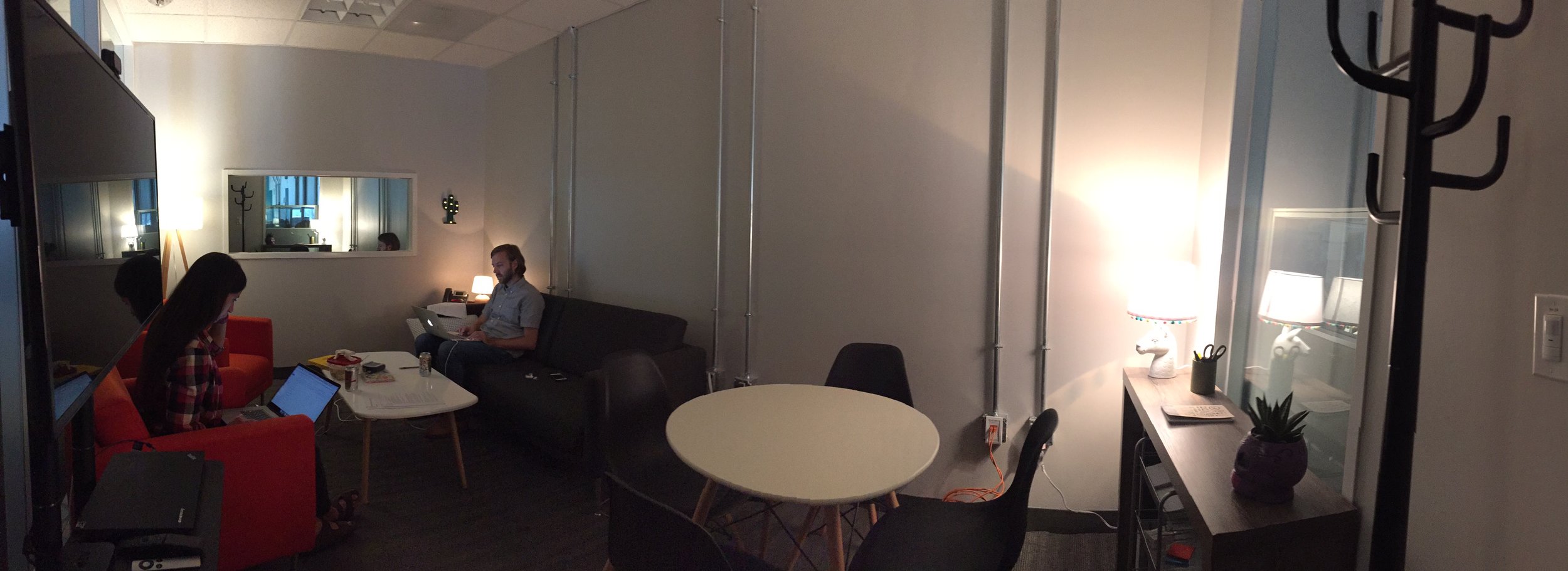











Equipment
The lab is complete with testing, viewing, and recording equipment allowing for a variety of research, usability testing, validation, and in-depth interviews.
Audio/video
The audio and/or video feed can also be transmitted to our conference rooms, which are large enough to accommodate your entire team. In these conference rooms, the team can both watch the sessions and easily discuss their observations with each other. For those who are unable to be on-site for testing, we stream the audio and video feeds over the Internet, so they can follow along on their personal computers or from your office.
These advanced labs make it possible for us to offer numerous user research services, including usability testing, rapid iterative testing, competitive testing, design walk-through testing, mobile and tablet testing and eye-tracking, to address a variety of research needs.
MULTILINGUAL TESTING SETUP
From time to time our clients need to test customers whose primary language is not English, which occurs frequently with in-country usability testing and remote usability testing. In this case the moderator asks questions in English, which are translated for the participant by an interpreter. The participant’s responses are then translated into English by the interpreter for the moderator and client. We can record either the English comments alone or both languages on the video. Additionally, in-house and remote observers can listen to the language of their choice; we can send the feeds for the different languages to separate conference rooms or stream the feeds over different phone connections.
The portable lab allows Macmillan to test outside the lab, at universities, community colleges, and other locations. With this flexibility, we can interact with students and instructors in their natural environment.
I set up a wide variety of services for testing on the road, including usability testing, rapid iterative testing, competitive testing, design walk-through testing, mobile and tablet testing. Also examined portable multilingual testing setup, for testing customers whose primary language is not English.
Participant Logistics
Collaborated with product managers, product designers, UX designers, and other researchers to strategize and design research activities using user-centered design. This included identification of user needs and goals, task and workflow modeling, ethnography and persona development.
I wrote the procedural manual for recruitment process & scheduling of participants. Streamlined participant onboarding, compensation and retention. Guided development of participant screeners that are relevant to each research project.
Biometrics
The journey to understand human behavior is a huge part of scientific study, from psychology experiments to consumer research and well beyond. While many of these fields of study have traditionally used a direct question and answer approach, real progress has been made by delving deeper. Biometric research provides the quickest and most accessible route to understanding how someone thinks, acts, and feels.
The best method available for understanding human behavior is therefore no single approach, but a combination of methods that integrate the best parts of each, providing an accurate and holistic view.
Surveys and focus groups have been a central part of human behavior research for decades, and are valuable in that they provide answers about an individual’s conscious thought process, and reasons for their actions. This can be valuable information, depending on your research question.
Understanding human psychology and behavior is at the cornerstone of a huge amount of research being conducted today. Unfortunately bad research methods and incorrect conclusions are still part of everyday life in both the academic and commercial world. The study of human behavior, in most cases, lacks not only the correct frameworks, but also the correct tools.
TIPS MOVING FORWARD FOR UX LABS
Wall paint
If your lab has one-way glass, you’ll want to paint your walls a very dark color- grey works well. The reason is this: if your viewing room is too bright, test participants may catch glimpses of you and your team moving around and watching them.
Lighting
Lighting needs to be just right. It’s important to keep lighting in the room dim. You’ll need to measure the maximum level of light available to you without inducing glass transparency and glare. An electronic dimmer switch, set to fade up to a tried-and-tested maximum, is useful.It’s a good idea to provide table-top LED downlights so that observers can discreetly light their devices and notebooks. It’s also worthwhile turning device screens down as the combined glare of several screens can push your room light up above bounds.Placement of your TV panel is important. It should be positioned in a way that doesn’t cast excess light in the direction of your glass.
Quiet
Soundproofing needs consideration too. Your observers need to be relatively quiet. I’ve seen labs provide headphones so that observers can turn audio volume up without sound leaking into the testing suite.










